Redundant Array of Impartial Disks (RAID) is a expertise for storage items that gives a balanced move and loads of advantages, akin to higher fault tolerance, enhanced reliability, and excessive efficiency.
It combines two or extra disk storage arrays into logical items that behave like a single drive. This gives The grouping is applied utilizing software program and {hardware}.
In easy phrases, RAID permits a number of arduous drives to couple with a single bigger storage capability disk.
Together with creating a bigger cupboard space from quite a few smaller drives, it additionally helps in numerous efficiency duties, akin to safety throughout drives to enhance write and browse velocity and mirroring for knowledge redundancy.
There are totally different RAID ranges out there to select from. RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 are the preferred ranges. Every degree is developed to perform a sure job.
This time period is kind of unfamiliar, and therefore, many individuals discover it difficult to make a correct choice on what to decide on between RAID 0 and RAID 1.
On this article, I’ll talk about RAID 0 VS RAID 1 and examine them that can assist you perceive the distinction between the 2 applied sciences.
Let’s begin!
What Is RAID 0?
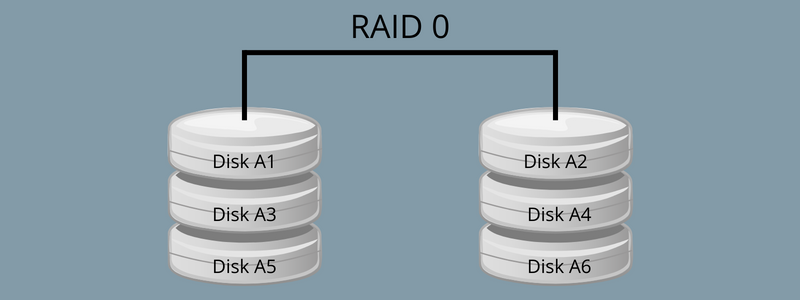
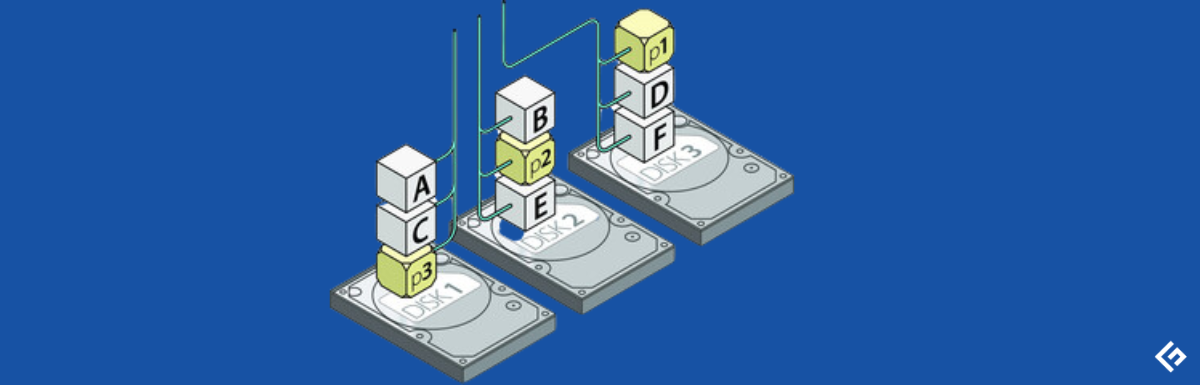
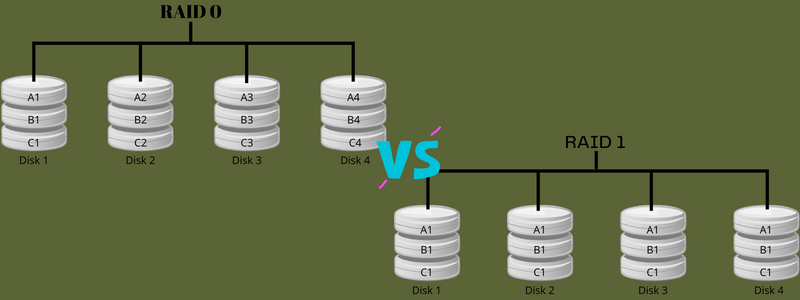
RAID 0 is a regular configuration that makes use of knowledge striping reasonably than parity and mirroring for dealing with knowledge. It’s the strategy of dividing knowledge into totally different blocks and spreading them throughout different storage units, akin to solid-state drives (SSDs) or arduous disks.
RAID 0 usually improves the system’s efficiency and depends totally on RAID for its operations. Additionally, it helps in creating a big logical quantity from varied units of small-capacity drives.
How Does RAID 0 Work?
A stripe consists of knowledge divided throughout SSDs or arduous disks, and the striped unit defines the information slice on the person drive. Since striping extends the information throughout bodily drives, totally different disks can entry contents, enabling reads and writes to finish sooner.
Disk striping, with out parity for dealing with knowledge, tends to have zero fault tolerance and redundancy. Because of this when a drive fails, all the information on the drive shall be misplaced. A system stripes knowledge on totally different ranges, akin to byte-level, bite-level, block-level, or partition-level.
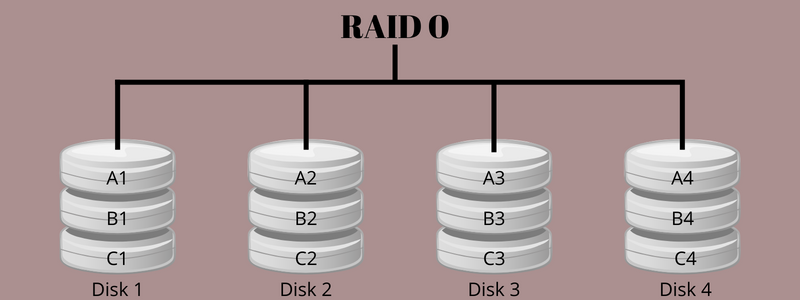
For instance, a storage system has ten arduous disks that strip a 64 KB block on the primary, second, third, fourth, and fifth disks. It restarts from the primary disk. Equally, the system strips 1 MB of knowledge on every of the ten disks and returns to the primary disks to repeat the process.
Thus, RAID 0 is without doubt one of the finest applied sciences used for storage. Although it’s non-critical, it requires high-speed writing and studying. Caching video modifying and stay streaming video are some use circumstances of RAID 0 because of its velocity and efficiency.
What Is RAID 1?
RAID 1, additionally known as disk mirroring, is cloning/copying knowledge to a number of disks. Purposes, akin to working methods, e mail methods, transactional functions, and so on., that require excessive availability and efficiency can leverage this disk mirroring.
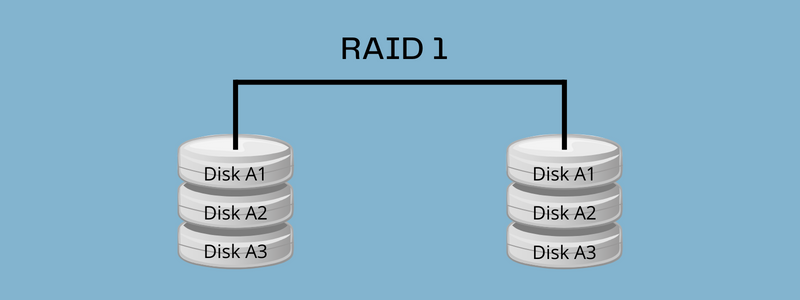
RAID 1 is essentially the most used RAID degree that goals to reinforce the safety of the saved knowledge. It used a easy idea of mixing two or extra arduous disks that retailer your knowledge in a replica method. This course of is named mirroring.
For instance, if a file is written and saved to 1 arduous disk, it’ll robotically be saved on arduous disk 2, 3, or different disks. Because of this the system gives full redundancy, which implies if one drive fails, the second is able to soar in.
How Does RAID 1 Work?
The RAID array works if one drive is lively and operational. As each the drives are operational, knowledge could be learn simply from them, which makes the operation quick. Since RAID 1 works nicely with SSDs for modern storage methods, many favor “drive monitoring”.
Nevertheless, writing operations are slower as every writing operation is completed twice. Throughout catastrophe restoration situations, one and solely disk mirroring is useful because it provides failover for the information that you just want for mission-critical functions.
If the first drive will get broken or just isn’t operational, site visitors immediately switches to the mirrored or secondary backup drives. Then, the mirror copy can turn out to be operational as a result of the applying software program and working system are cloned to the drive together with the knowledge by the functions.
RAID 0 vs. RAID 1: Benefits and Limitations
Now that about RAID 0 and RAID 1 let’s talk about some benefits and limitations of each applied sciences.
Benefits of RAID 0
- Enhanced efficiency: RAID 0 gives greater velocity and efficiency. Let’s perceive this with an instance. When the information is striped throughout three units, it gives thrice extra bandwidth. If we assume each drive runs at 250 Enter Output Operations per second, the setup can have 750 IOPS, making it tremendous quick for you.
- No overhead: The whole capability of every drive is used for storing as RAID 0 doesn’t use parity disks.
- Straightforward to implement: You don’t want many expertise to arrange a RAID 0 degree, making it faster and simpler to implement.
- Low price: The configuration price of RAID 0 is lesser and is supported by the RAID controllers.
- Bandwidth: The bandwidth of RAID 0 is larger than single drives.
- Storage Capability: It makes use of the whole storage capability
Limitations of RAID 0
The principle limitation of RAID 0 is that there isn’t a parity, leading to no fault tolerance. In case your knowledge is misplaced or corrupted for some purpose, there isn’t a backup or resiliency, making it unimaginable to retrieve any knowledge.
The chance of failure with RAID 0 is greater than with single drives. Subsequently, it’s thought of the best alternative for crucial methods.
Benefits of RAID 1

- Knowledge redundancy: The foremost benefit of RAID 1 expertise is knowledge redundancy as a result of knowledge is duplicated throughout two or extra disks.
- Fault tolerance: For essentially the most mission-critical functions, one of these knowledge storage is most-suited. When one drive fails, one other drive takes over the first obligation. Since each drives embrace an identical knowledge, the customers don’t have any impression.
- Excessive efficiency: The information you utilize could be learn from a number of units concurrently. Therefore, it’s comparatively sooner.
- Excessive availability: Knowledge is mirrored throughout two or extra disks. So on the time of want or catastrophe restoration situation, you may simply retrieve the information. Therefore, the opportunity of shedding knowledge is slender.
- Excessive safety: From a safety viewpoint, RAID 1 gives knowledge safety by copying knowledge at a number of locations. Suppose one among your methods is hacked and also you lose knowledge; you may nonetheless entry one other.
Limitations of RAID 1
RAID 1 finds utilization in lots of sectors because of its mirroring performance. This degree performs an important function in securing your knowledge from private to enterprise use. However it nonetheless has some limitations.
- No real-time swapping: When the primary disk fails, the secondary disk doesn’t take the function instantly or robotically. It must be restarted, which is a bit of little bit of an inconvenience.
- Costly: RAID 1 requires extra space to implement. Thus, it’s extra expensive in comparison with RAID 0.
- Diminished storage capability: Should you use two disks at a time and each include the identical knowledge, your total capability will get halved.
- Efficiency: Learn and write efficiency in RAID 1.
RAID 0 vs. RAID 1: Similarities
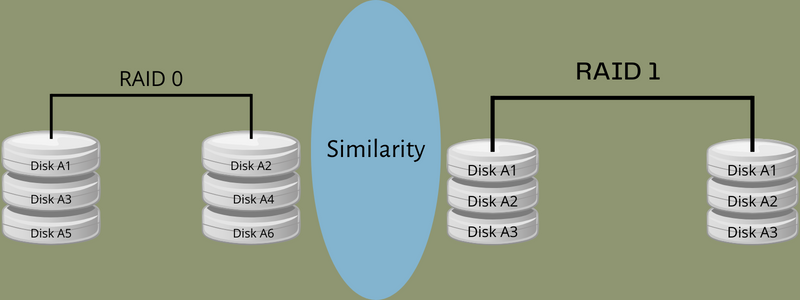
There are a couple of similarities between RAID 0 and RAID 1 when it comes to build-up and wishes. But, they’re totally different of their performance of storing knowledge. Let’s see what they’re:
- RAID 0 and RAID 1 are array ranges.
- The first use of each RAID ranges is direct knowledge administration of the disk drives.
- Each applied sciences had been conceived in 1987 and launched in 1988.
- RAID 0 and RAID 1 are open codecs.
- The applied sciences utilized in these ranges are servers, virtualization, and arduous drives.
- The minimal variety of disks required is 2 for each arrays.
RAID 0 vs. RAID 1: Variations
The most important variations between the 2 ranges are their main knowledge storage capabilities. RAID 0 and RAID 1 deal with their storage units in a different way. RAID 0 places all of the drives within the RAID array right into a single logical quantity, whereas RAID 1 copies the first drive to a number of drives within the array in actual time.
This makes RAID 0 the quickest storage drive for studying and writing operations at a a lot decrease price. In distinction, RAID 1 turns into the safer possibility for enterprises for his or her knowledge integrity and security. Since each are full of benefits of their path, it is going to be difficult to resolve which one to decide on.
The easy but highly effective possibility could be the real-world utilization of every array. This implies the place there’s a threat of failure or safety; it’s worthwhile to give attention to RAID 1. In some circumstances, like PC gaming and 3D modeling, the place you want the quickest velocity in studying and writing operations, RAID 0 is the best choice.
Let’s perceive the key variations between RAID 0 and RAID 1 facet by facet:
| RAID 0 | RAID 1 |
| RAID 0 means Redundant Array of Impartial Disk degree 0. | RAID 1 means Redundant Array of Impartial Disk degree 1. |
| Within the RAID 0 array, disk striping is the first operation. | In RAID 1, disk mirroring or duplication is the first operation. |
| The associated fee is comparatively decrease. | It’s expensive as in comparison with RAID 0. |
| No write penalty. | There’s a written penalty. |
| The relative storage capability is 100%. | The relative storage capability is 50 %. |
| The learn and write efficiency, together with velocity, is excessive. | The learn and write efficiency and velocity are slower than RAID 0. |
| It emphasizes knowledge accessing velocity. | It emphasizes knowledge availability. |
| There isn’t a safety. | You’ll discover mirror safety. |
| There isn’t a redundancy, fault tolerance, and mirroring facility. | You’ll get redundancy, mirroring, and fault tolerance. |
| It’s used when the information reliability is much less involved, however velocity is essential. | It’s used when knowledge loss just isn’t acceptable. |
| Knowledge is unrecoverable. | Knowledge could be rapidly recovered in a catastrophe restoration program. |
| Knowledge is saved in a single place. | Knowledge could be saved in a number of locations. |
| Two disks include two totally different units of knowledge. | Two disks include comparable units of knowledge. |
RAID 0 vs. RAID 1: When to Use Every?

RAID 0
- Should you want one hundred pc storage capability and knowledge loss just isn’t an enormous downside, RAID 0 is the best choice because it’s cheaper.
- If it’s worthwhile to create a logical quantity on high of the volumes, akin to creating volumes on RAID-protected LVM in Linux servers, the RAID 0 degree is ideal.
- If one other type of knowledge safety is offered, akin to reproduction copy, community RAID, and so on., within the occasion of shedding knowledge, RAID 0 is a greater possibility for private use like PC gaming.
RAID 1
- If knowledge redundancy is your main want, RAID 1 shall be higher.
- If storage capability and finances aren’t main points however safety is, RAID 1 degree is preferable.
- It’s best appropriate for mission-critical functions.
- If you need excessive Enter Output Operations per Second (IOPS), go along with RAID 1.
Combining RAID 0 and RAID 1
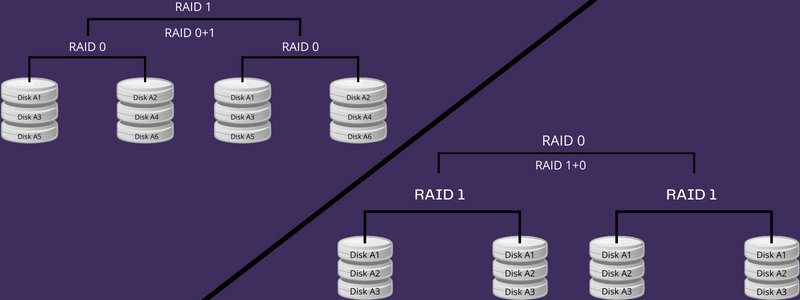
Two ideas could be mixed individually to make one of the best use of each applied sciences in numerous areas. Should you mix RAID 0 and RAID 1, you may create two mixtures:
- RAID 01 (RAID 0+1)
- RAID 10 (RAID 1+0)
The extent that comes first within the mixture has its perform and is later used because the second perform of the second degree. RAID 0 and RAID 1 mix to make a strip of mirrors, whereas RAID 1 and RAID 0 are related to make a mirror of strip configuration.
These mixtures are referred to as nested RAID ranges. Since RAID 10 comes with higher fault tolerance, it’s extensively utilized in many enterprises. It combines disk mirroring and disk striping ideas to concurrently use 100% storage capability and knowledge safety. This manner, you may retailer increasingly knowledge with out shedding any knowledge, even throughout a catastrophe restoration program.
Conclusion
Selecting between RAID 0 and RAID 1 could be tough. It’s not a matter of expertise, nevertheless it largely relies on your use case.
RAID 0 gives no redundancy and makes use of striping, which implies knowledge is cut up throughout a number of drives to learn or write knowledge at excessive velocity. Alternatively, RAID 1 gives knowledge redundancy by means of knowledge replication which implies knowledge is written equally to 2 or extra drives making it prepared for any catastrophe. However, RAID 1 is barely slower as in comparison with RAID 0.
You see, each ranges work fairly nicely in numerous use circumstances. RAID 0 is usually a better option while you want the efficiency over redundancy. And when it’s worthwhile to deal with mission-critical methods, RAID 1 could be higher. So, select RAID 0 or RAID 1 based mostly in your necessities.
You may additionally discover some finest Community Connected Storage (NAS) options for versatile knowledge backup and safety.