Know the way a lot a person course of or system-wide is consuming CPU or reminiscence.
As a system administrator, you usually encounter an incident the place the applying is gradual or unresponsive attributable to excessive CPU/reminiscence/community utilization. If the server hosts just one course of, it’s straightforward to seek out out when the method consumes all of the assets. Nonetheless, think about a shared server working a number of companies, and it’s worthwhile to work out which one is consuming up all of the assets.
There are various monitoring software program that do that out of the field. But when you do not have one or are in search of a command-based answer, right here you might be. They’re all FREE!
high
You might need to begin by it high or htop consequence to see the method overview.
As you possibly can see under, it offers a superb thought of what all of the processes are utilizing. In case you take a look at the primary one, which is MySQL, it takes up 11.9% of the CPU and a pair of.5% of the CPU.
high - 11:57:33 up 0 min, 1 consumer, load common: 3.69, 0.96, 0.32
Duties: 165 complete, 2 working, 113 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 21.0 us, 5.5 sy, 0.0 ni, 70.5 id, 1.7 wa, 0.0 hello, 1.3 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 7637308 complete, 5802888 free, 849512 used, 984908 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 0 complete, 0 free, 0 used. 6495648 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
1986 netdata 20 0 1738856 191560 22948 S 11.6 2.5 0:02.30 mysqld
3021 www-data 20 0 255288 78420 55484 S 6.6 1.0 0:01.55 php-fpm
3138 www-data 20 0 253096 79780 59228 S 6.6 1.0 0:00.92 php-fpm
3153 www-data 20 0 255116 79088 56472 S 5.0 1.0 0:00.70 php-fpm
3037 www-data 20 0 257200 81088 56216 S 4.3 1.1 0:01.50 php-fpm
3048 www-data 20 0 257088 78740 55380 S 4.3 1.0 0:01.46 php-fpm
3054 www-data 20 0 254160 72168 52108 S 3.7 0.9 0:01.32 php-fpm
3135 www-data 20 0 255084 75912 54836 S 3.7 1.0 0:00.91 php-fpm
3051 www-data 20 0 254096 73804 51964 S 3.0 1.0 0:01.38 php-fpm
2962 www-data 20 0 45280 7284 3488 R 2.0 0.1 0:00.22 openresty
1062 netdata 20 0 338748 76144 6720 S 1.0 1.0 0:01.31 netdata
1702 netdata 20 0 21852 4232 2352 S 1.0 0.1 0:00.34 apps.plugin
1729 netdata 20 0 18636 3280 2764 S 0.7 0.0 0:00.05 bash
1980 netdata 20 0 62008 12896 5796 S 0.7 0.2 0:00.14 redis-server
11 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.3 0.0 0:00.14 rcu_sched
1007 root 20 0 1347424 74524 38872 S 0.3 1.0 0:00.92 dockerd
1857 root 20 0 10600 5564 4276 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.03 containerd-shim
2045 root 20 0 9948 6028 5016 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.14 forego
2934 root 20 0 13616 8760 5928 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.07 docker-gen
2966 systemd+ 20 0 25784 7924 2340 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.06 nginxThe high is put in on virtually all Linux distributions.
As soon as you have recognized the suspect, chances are you’ll need to deal with that course of as an alternative of the whole lot else such as you noticed above. You may nonetheless use high command, however with an argument.
Say you understand the method ID (PID); you should utilize the command under.
high -p $PID
Under is an instance of this high -p 3102
high - 11:59:56 up 3 min, 1 consumer, load common: 0.72, 0.70, 0.31
Duties: 1 complete, 0 working, 1 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 7.1 us, 2.9 sy, 0.0 ni, 89.1 id, 0.3 wa, 0.0 hello, 0.7 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 7637308 complete, 5802024 free, 783672 used, 1051612 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 0 complete, 0 free, 0 used. 6555636 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
3102 www-data 20 0 329500 82376 60640 S 0.0 1.1 0:03.35 php-fpmYou might also use grep of high. Under is an instance of checking Docker utilization.
root@geekflare-com:~# high | grep docker
1007 root 20 0 1347424 74524 38872 S 0.3 1.0 0:01.38 dockerd
2934 root 20 0 14676 9652 5928 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.54 docker-gen
1007 root 20 0 1347424 74524 38872 S 0.3 1.0 0:01.39 dockerd
1007 root 20 0 1347424 74524 38872 S 1.0 1.0 0:01.42 dockerd
2934 root 20 0 14740 9652 5928 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.55 docker-gen
2934 root 20 0 14740 9652 5928 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.56 docker-genhtop
Just like the highest, however with extra info. As you possibly can, it has been given a command column, which is helpful for figuring out the method path. And additionally it is colourful.
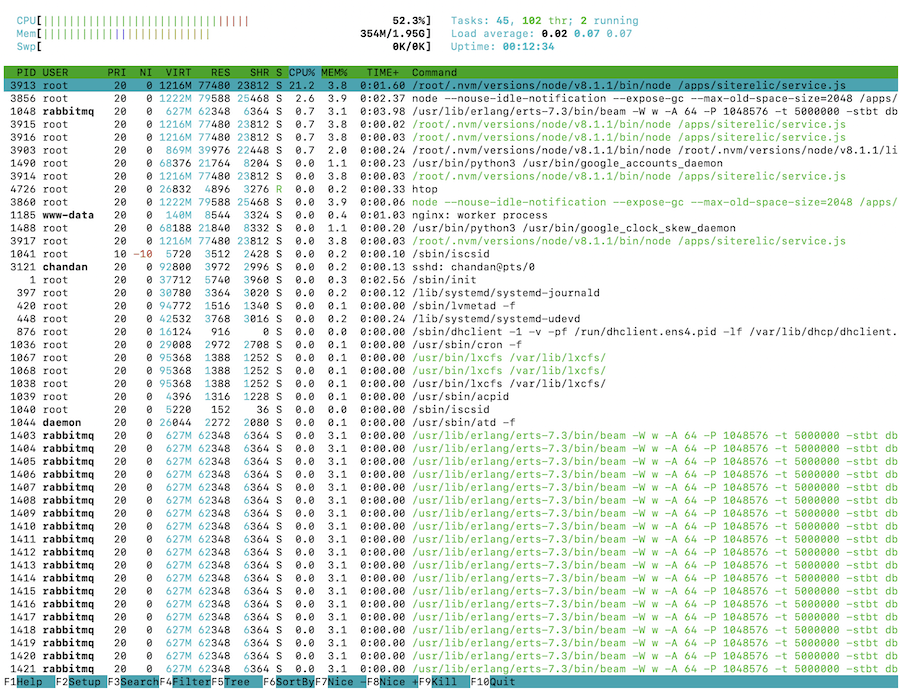
htop will not be put in by default, however you possibly can all the time do it as under.
Set up htop on Ubuntu
apt-get set up htopSet up htop on CentOS/RHEL 8.x
dnf set up https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
dnf replace
dnf set up htopcans
Because the title says, you get a view of the system utilization on one display screen. Working processes are sorted by CPU utilization.
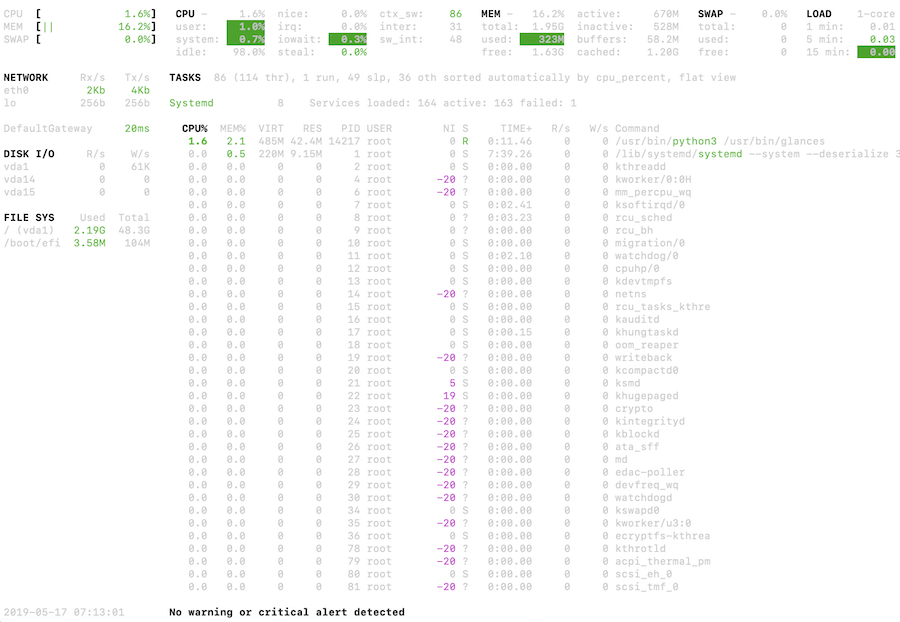
You may set up cans on CentOS 8 utilizing DNF as under.
dnf set up glancesfor CentOS7 you should utilize YUM
yum set up glancesabove
One much like those talked about above however with an excellent function to file the outputs to a file so you possibly can watch them later. Think about there’s a sample of getting an issue in a particular time-frame. You may schedule to jot down the output to a file through crontab or one thing else, and you may play it again later.
To place the output right into a file:
atop -w filenameand, to play:
atop -r filenameIt helps a number of arguments like interval, samples, and so forth. and I might extremely advocate you take a look at the person web page.
In case you’re solely inquisitive about real-time troubleshooting, simply run it atop and you must see it like under.
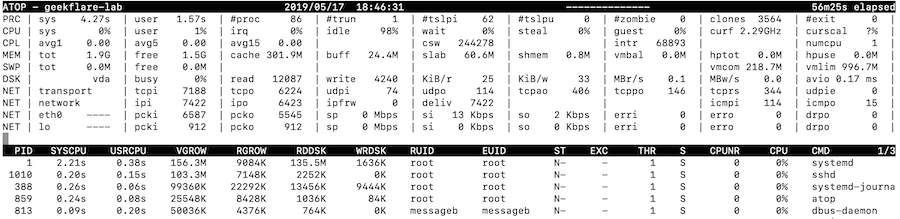
You may set up on high of it as under.
dnf set up atopPS
Let’s examine ps command now.
You should use the ps command with PID to print their CPU and reminiscence utilization.
ps -p $PID -o %cpu,%memThe output ought to appear to be this.
root@sr-master-us:~# ps -p 1048 -o %cpu,%mem
%CPU %MEM
0.2 3.0
root@sr-master-us:~#no
Interactive command line monitoring device for CPU, reminiscence, disks, community, NFS and digital reminiscence utilization. To view the highest course of (by use), you possibly can run nmon and press t knob.
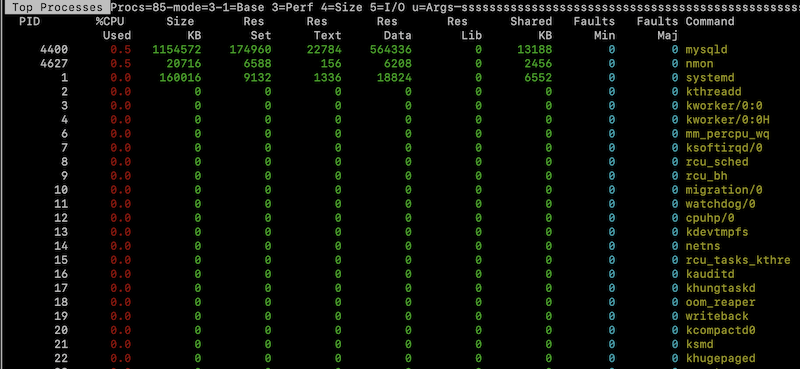
You may set up nmon as under.
dnf set up nmonquick
Monit is a web-based and command line open supply answer for monitoring server assets, daemons, recordsdata, directories, file programs, and so forth.
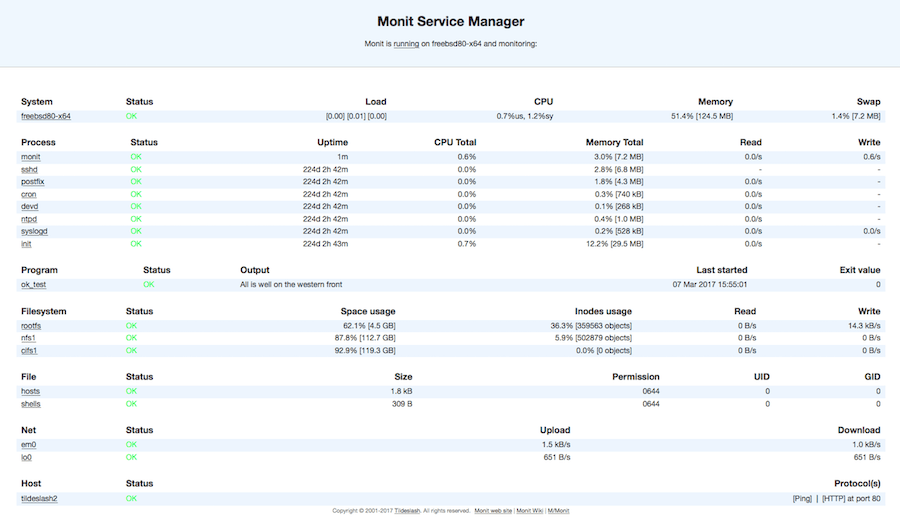
Monit additionally obtained a cool widget.
The light-weight monitoring software program. However there may be much more to find right here.
Monitorix
A light-weight open-source utility to observe Linux server. Monitorix has built-in HTTP so you possibly can monitor utilization and different issues on the Web. A number of the different utilization studies embody:
- core/temperature
- File system and I/O
- Community site visitors
- Apache/Mail/FTP/Nginx
- MySQL/Varnish/Memcached
Monitorix additionally presents alert configuration so that you will be notified if one thing is fallacious. It is a sensible choice when you handle cloud-based servers and are in search of a proactive monitoring answer.
Community information
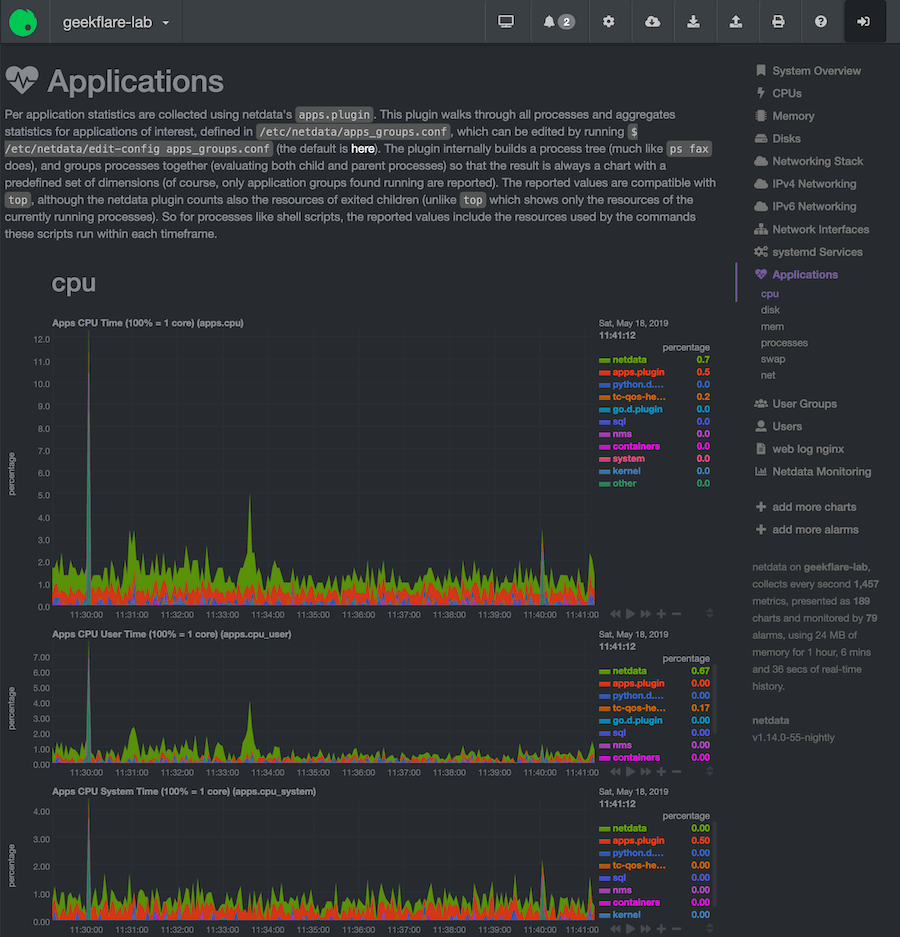
Netdata is a real-time efficiency monitor for system assets, functions, net servers, databases, DNS, mail, {hardware} sensors and way more. It is open-source and getting began is simple. All information is collected, saved and streamed so to visualize it interactively. Information is collected each second, so that you by no means miss a factor.
Cherished by many trade leaders.
So what you might be ready for, attempt to take management of your Linux servers.
btop
btop is a useful useful resource monitor that’s totally interactive with a fantastic consumer interface that helps you handle the Linux servers.
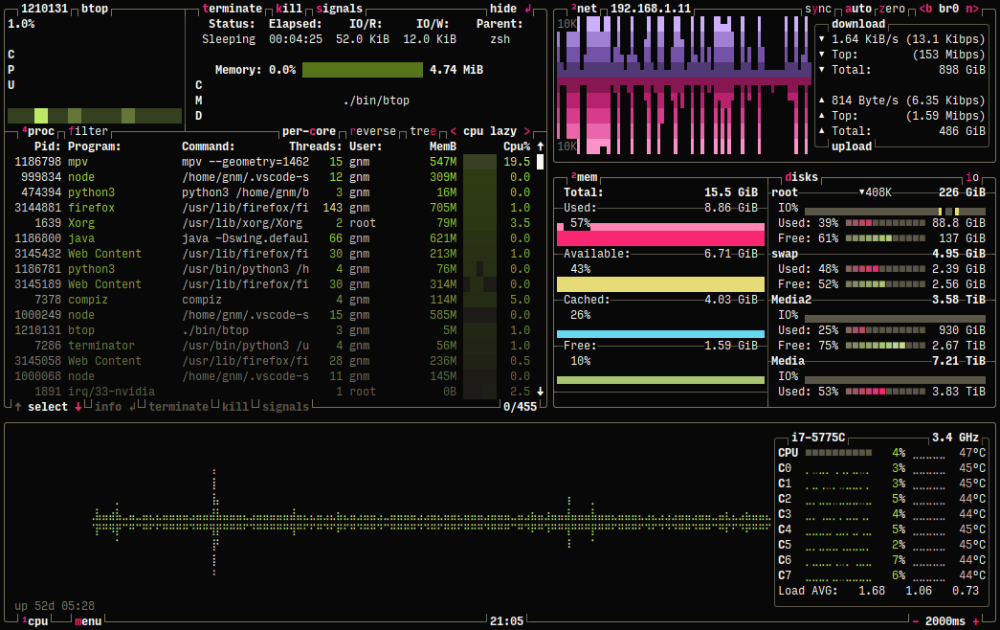
You may simply visualize the processes in a tree construction, filter from the method record and handle the useful resource pigs. btop additionally comes with an auto-scaling graph that shows community utilization.
As well as, you may also examine the disk pace and full the I/O exercise.
There may be extra you possibly can expertise on Linux, FreeBSD and macOS.
Conclusion
I hope the instruments above show you how to visualize server utilization in actual time so you possibly can take the mandatory motion. In case you’re simply beginning out as a system administrator and in search of hands-on coaching, take a look at this Udemy course.

